


Here are complete detail of logical venn diagram topics for those students who are preparing for the competitive exams. This topic related to reasoning section. Here students easily understand this topic through venn diagram types, problems and their solutions also by the different-2 examples.
You should understand or practice this topic to obtain good marks in the competitive exams as well to improve your performance. After knowing complete about this topic, you can practice with important logical venn diagram questions by one click.
A geometrical represent between two articles on the basic of set theory known as Venn diagram.
This section deals with the question which aim at analyzing a candidates ability to relate a certain given group of items and illustrate it diagrammatically.
Here are a few different types of Venn diagrams with their implication made clear. Suppose you are given a group of three item. Then
Type.1. if the items evidently belong to three different groups, the Venn diagram representing it would be as shown alongside.
Ex. Doctors, Engineers, Lawyers
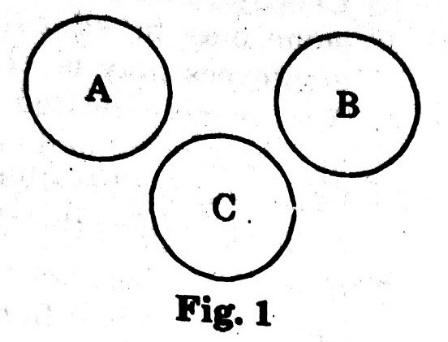
These three items bear no relationship to each other. So, they are represented by 3 disjoint figures as shown in Fig. 1.
Type.2. if one item belongs to the class of the second and the second belongs to the class of third, then the representation is in the form of three concentric circles, as shown in Fig. 2.
Ex. Seconds, Minutes, Hour’s
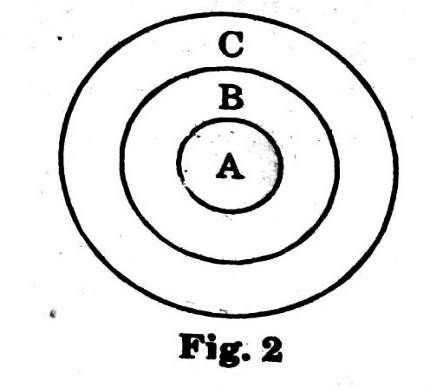
Clearly, seconds are a part of minutes and minutes are a part of hours. So, the Venn diagram would be as shown in the adjoining figure with circle A representing Seconds, circle B representing Minutes and circle C representing Hours.
Type.3. if two separate items belong to the class of the third, they are represented by two disjoint circles inside a bigger circle as shown in Fig. 3.
Ex. Table, Chair, Furniture
Clearly, table and chair are separate items but both are items of furniture. So, they would be represented as in the adjoining figure with circle A representing Table, circle B representing Chair and circle C representing Furniture.
Type.4. if two items belong to the class of the third such that Some items of each of these two groups are common in relationship, then they are represented by two intersecting circles enclosed within a bigger circle.
Ex. Males, Fathers, Brothers
Clearly, some fathers may be brothers and vice-versa. So, fathers and brothers would be represented by two intersecting circles. Also, both fathers and brothers are males. So, the diagrammatic representation would be as shown in Fig. 4, with circle A representing Fathers, circle B representing Brothers and circle C representing Males.
Type.5. if two items are partly related to the third, and are themselves independent of each other they are represented by three intersecting circles in a line.
Ex. Dogs, Pets, Cat
Clearly, some dogs and some cats are pets. But all the pets are not dogs or cats. Also, dogs and cats are not related to each other. So, the given items would be represented as shown in fig. 5 with circle A representing Dogs, circle B representing Pets and circle C representing Cats.
Type.6. if the three items are partly related to each other, they are represented as shown in the adjoining figure.
Ex. Clerks, Government Employees, Educated Persons
clearly, some clerks may be government employees and Some may be educated. Similarly, some government employees may be clerks and some may be educated. Also, some educated persons may be clerks and some may be government employees. So, the given items may be represented as shown in Fig. 6 with three intersecting circles denoting the three classes
Type.7. if one item belongs to the class of second while third item is entirely different from the two, then they may be represented by the adjoining diagram.
Ex. Engineers, Human Beings, Rats
Clearly, all engineers are human beings. This would be represented by two concentric circles. But the class of rats is entirely different from these two. Thus, these items would be represented as shown in Fig. 7 with circle A representing Engineers, circle B representing Human Beings and circle C representing Rats.
Type.8. if one item belongs to the class of second and the third item is partly related to these two, they are represented as shown alongside.
Ex. Females, Mothers, Doctors
Clearly, all mothers are females. This would be represented by two concentric circles. But, some females and some mothers can be doctors. So, the circle representing doctors would intersect each of the two concentric circles. Thus, the diagram becomes as shown in Fig. 8 with circle A representing Mothers, circle B representing Females and circle C representing Doctors.
Type.9. if one item belongs to the class of second and the third item is partly related to the second, they are represented as shown alongside.
Ex. Males, Fathers, Children
Clearly, all fathers are males. This would be represented by two concentric circles. But, some males are children. But, children cannot be fathers. Thus, the diagram becomes as shown in Fig. 9 with circle A representing Fathers, circle B representing Males and circle C representing Children.
Type.10. If two items are partly related to each other and the third item is entirely different from the two, they are represented as shown alongside.
Ex. Professor, Author, Children
Clearly, some professors can be authors and vice versa. This would be represented by two intersecting circles. But the class of children would be entirely different from these two. Thus, the Venn diagram would be as shown in Fig. 10 with Circle A representing Professors, Circle B representing Authors and circle C representing Children.
Get the Examsbook Prep App Today